What is CBG
So far we have heard and seen a lot about CBD, but lately, another substance has received more attention: CBG. But what exactly is that? Let me explain what you need to know about CBG and its benefits.
CBG or cannabigerol is being studied for its potential pharmacological properties. However, it has not been in any clinical preliminaries thus far. Only one examination of CBG has been made in the 60s, even though the plant is thousands of years old, meaning that most of the knowledge we have about CBG is fairly new.
Cannabigerol or CBG is the precursor, respectively the first cannabinoid that is formed in the plant and which later is used to produce CBD, CBC, and THC. Basically, CBG is the stem cell.
After the acidic, inactive form of CBG has transformed and been broken down, it becomes the base molecule from which other cannabinoids can be formed (such as CBD, THC, CBC). However, in most cannabis varieties only <1% of cannabigerol is found. Therefore it is not very surprising that this has not attracted as much attention as other cannabinoids.
CBG is non-psychoactive, contains low THC, and is very high on CBD strains. CBD reacts with cannabinoid receptors just like THC, however, it acts as a buffer to psychoactive cannabinoids like THC helping for instance with paranoia.
CBD vs CBG
While CBG and CBD are both cannabinoids, the difference lies in the compounds within the actual cannabis plant. CBG does not always treat the same issues as CBD. CBG, or rather the acid from CBGA, is the first cannabinoid acid that is produced in the cannabis plant. The acid form is the CBG molecule with an additional carboxyl group – this is also what the “A” in the abbreviation CBGA stands for. As the plant continues to grow, CBGA is converted by enzymes into THCA, CBDA, or CBCA.
The next step that the plant goes through is called decarboxylation. This is where the flowers are dried and processed. The heat or UV light applied to the flowers causes them to decompose, leaving behind the non-acidic equivalents of the acidic cannabinoids. This results in CBD, CBC, and THC, for example, and these are the most well known, there are at least 100 different cannabinoids that have their origin in CBGA.
As the plant converts, it is rather difficult to extract CBG as most plants have less than 1% of CBG for harvesting. This is why most manufacturers have only recently started to focus on CBG levels in cannabis and CBD products such as oils, creams, and food supplements.
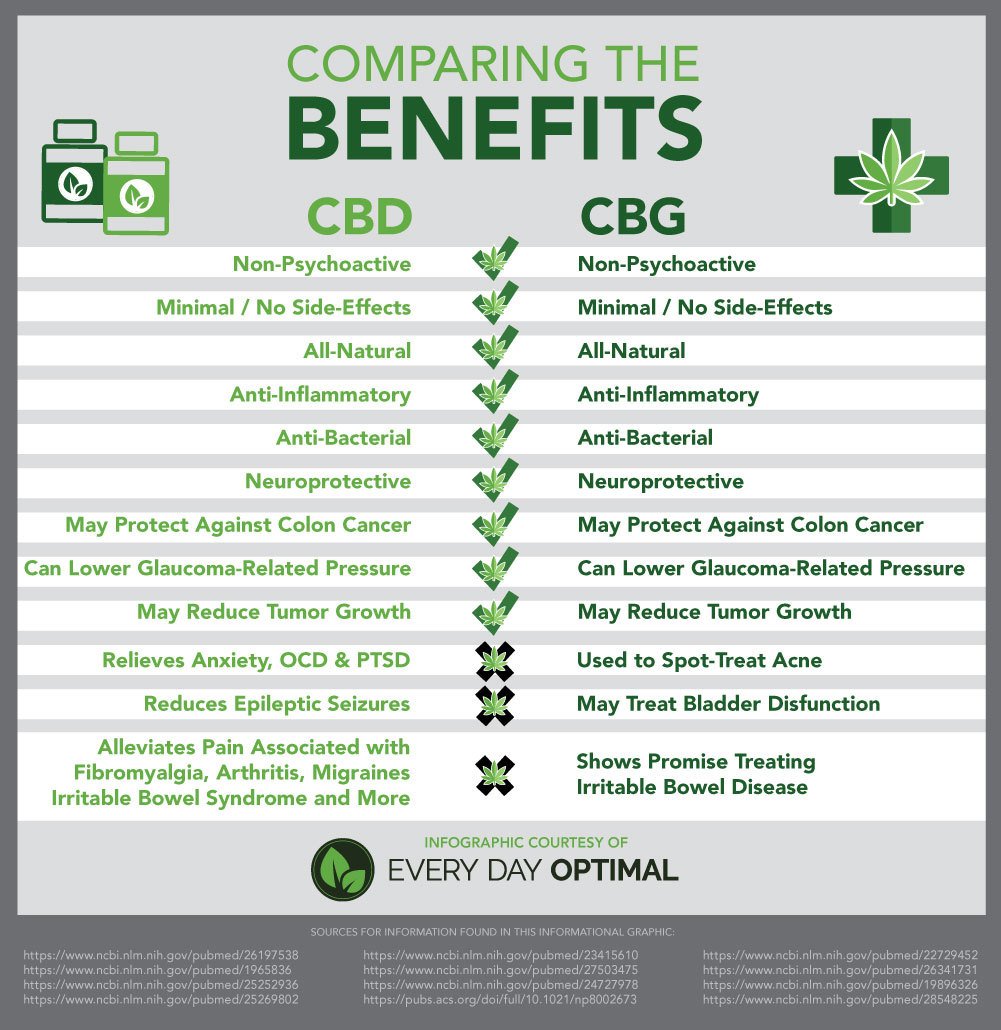
CBG vs CBD benefits (Source MinistryofHemp.com)
What are the benefits of CBG
CBG is not psychoactive, which means it is one of the non- intoxicating cannabinoids. CBD reacts with cannabinoid receptors (just like THC), acting as a buffer for paranoia caused by psychoactive substances like THC.
CBG has many other advantages, which are currently being researched further. One of them is that CBG may help with cancer, neurodegeneration, and colitis. It is also thought to be beneficial when fighting inflammation, pain, and nausea. One of the most interesting benefits is that CBG may help treat glaucoma and relieve intraocular pressure, which CBD on its own does not help with, however, CBG and THC do. It is also believed that CBD may work for Huntington’s and neurodegenerative diseases.
Dr. Goldstein from Shape.com says that CBG can normalize the expression of abnormal genes linked to brain degeneration. In two studies carried out in 2016 and 2017 at the University of Reading (UK), rats were used to show that CBG also increases appetite.
There is still much that has yet to be discovered but thus far CBG seems to be a very useful substance.
So, that’s everything you need to know about CBG and its benefits.
Source:https://www.shape.com/lifestyle/mind-and-body/what-is-cbg-vs-cbd

